Conservative radio host Lars Larsen missed the mark.
In an Oct. 24 column about the impending strike by Portland Public School teachers, Larson said the district “… spends 15-thousand bucks, per student, per year.”
He’s off by a mile.
I’m not surprised, though, that he used the $15,000 figure. That number is frequently cited in news stories. It is also close to the number put out by the National Center for Education Statistics, which estimates the per pupil expenditure in Oregon’s K-12 public schools for 2019-2020 was $14,829.[1]
Earlier this year I asked the Portland Public School District if that number still holds. The district said the average of budgeted per pupil expenditures for next year (2023-2024) is actually $11,000 per student.
“This represents standardized site services. (teachers, principals, counselors, etc,” the district explained. “It does not include services like transportation, nutrition, SpEd, ESL or other central office supports and operations. “
So, is Larson’s number too high? is $11,000 actually the answer?
Nope.
Now stay with me.
“Once you include services like transportation, nutrition, SpEd, English as a Second Language Programs (ESL), other central office supports and operations, from a whole system perspective the budgeted per pupil expenditure number doubles and is closer to $22k/student (this is both GenFund and Special Revenue and does not include bond dollars).,” the District told me.
This is getting confusing. Is $22,000 the final number then?
Nope, again.
It’s not so much a lie as an obfuscation, a deceit.
A lot of things PPS spends money on are not counted in calculating spending per student. When all spending is thrown into the pot, the spending per student jumps up substantially.
Let’s look at the 2022-2023 school year.
PPS served 41,470 students that year. At $22,000 per student, that would translate to total spending of $912.3 million. But the District’s 2022-2023 budget is actually $1.883 billion.
Why the huge difference?
Put simply, the $22,000 doesn’t take into account all funds that support the District each year. The table below, provided by the District, shows all resources available to the district for the school years 2018-19 through 2022-23.
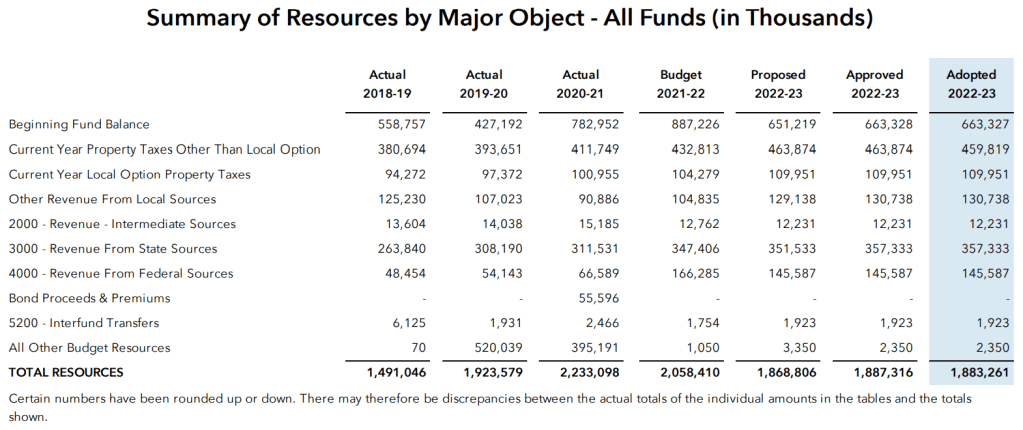
This table shows that all funds available to the District in the 2022-23 school year actually totaled $1.9 billion. divide that by 41,470 students and per student expenditures comes out to $45,533. That’s right, $45,533.
And that was more than the District spent per student in the 2021-22 school year, even though the number of students served declined.
In the fall of 2021, the District enrolled 45,005 students in grades K-12, a decrease of 1,932 students from fall 2020. The net loss was even greater than the previous year’s loss of 1,716 students.
A recent “Portland Public Schools Enrollment Forecast” by Portland State University’s Population Research Center projected that the District’s enrollment will likely continue to fall throughout most of the forecast’s horizon, declining to a low of 39,123 in 2035-36.
In the meantime, Angela Bonilla, president of the Portland Association of Teachers, is arguing , “We’ve been sounding the alarm to the district for nearly a year in bargaining sessions, but Portland Public Schools management has not been willing to fund what our schools need…”
And the beat goes on.
[1] According to the National Center for Education Statistics, the $14,829 of per student expenditures comprise expenditures for the day-to-day operation of schools and school districts for public elementary and secondary education, including expenditures for staff salaries and benefits, supplies, and purchased services. General administration expenditures and school administration expenditures are also included in current expenditures.
Expenditures associated with repaying debts and capital outlays (e.g., purchases of land, school construction, and equipment) are excluded from current expenditures. Programs outside the scope of public prekindergarten through grade 12 education, such as community services and adult education, are not included in current expenditures. Payments to private schools and payments to charter schools outside of the school district are also excluded from current expenditures. The Center says researchers generally use current expenditures instead of total expenditures when comparing education spending between states or across districts because current expenditures exclude expenditures for capital outlay, which tend to have dramatic increases and decreases from year to year. Also, many school districts support community services, adult education, private education, and other nonelementary-secondary programs, which are included in total expenditures. These programs and the extent to which they are funded by school districts vary greatly both across and within states and school districts.




